In any industry or organization, problems are bound to arise. Whether it is a manufacturing defect, a customer complaint, or an operational issue, it is essential to have a systematic approach to problem-solving and continuous improvement. That is where the power of 8D comes in. The Eight Disciplines (8D) approach is a structured problem-solving methodology that has proven to be highly effective in identifying root causes, implementing corrective actions, and preventing the recurrence of issues. This blog post will unveil the Eight Disciplines approach and explore each step in detail. From defining the problem and forming a team to implementing and verifying long-term solutions, get ready to unlock the power of 8D and take your problem-solving skills to the next level.
What are the Eight Disciplines (8D)?
The Eight Disciplines, or 8D, is a problem-solving methodology widely used in various industries to address complex issues and improve organizational performance. Developed by the Ford Motor Company, the 8D process provides a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems in a structured manner. It is used in industries that prioritize quality control, customer satisfaction, and ongoing improvement.
It encompasses eight steps, each designed to guide teams through problem-solving. This article will delve into each of the eight disciplines, outlining their purpose and significance within the problem-solving process.
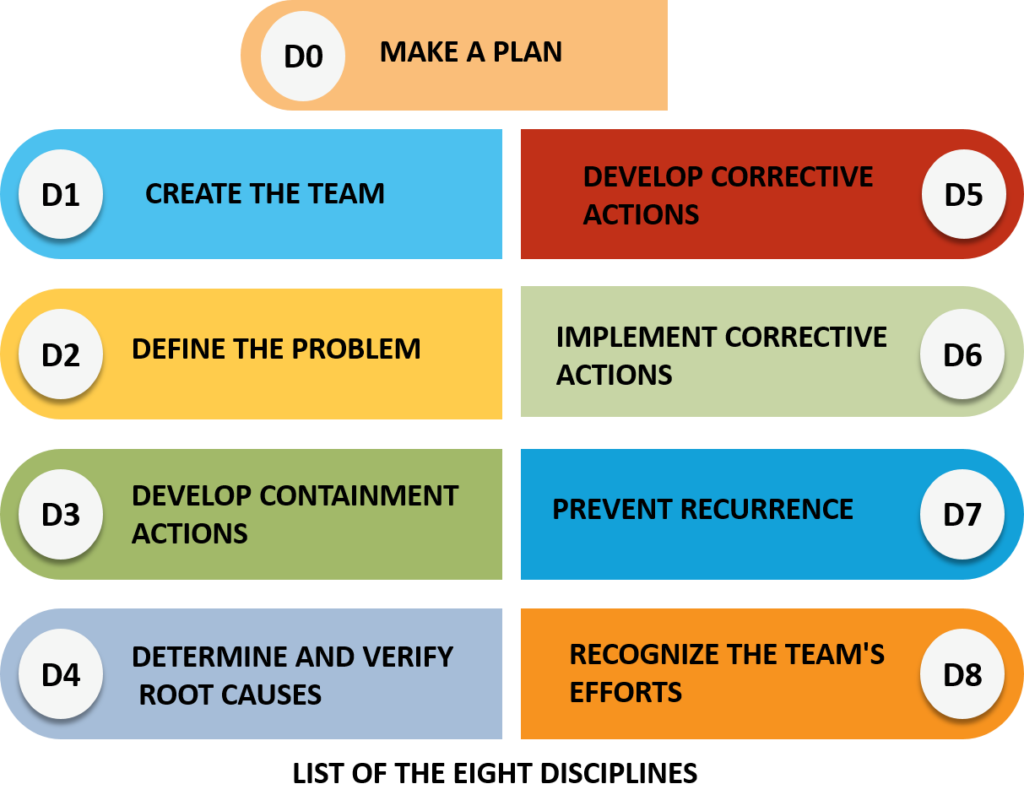
D0: Make a plan
D0 discipline is the initial step before the Eight Disciplines (8D) process starts. It involves setting up a plan to solve the problem and identifying what you need to get started. It is like making a roadmap before you begin your journey to address a complex issue.
D1: Create a Team
The first discipline, D1, emphasizes assembling a diverse team of individuals with relevant skills and expertise. These team members should possess varied knowledge to tackle the problem comprehensively. A diverse team ensures that it considers different perspectives and insights, leading to more robust problem-solving outcomes.
D2: Define the Problem
In discipline D2, the focus is on clearly defining the problem at hand. This involves specifying the problem’s scope, understanding its implications for the organization, customers, or stakeholders, and establishing clear objectives for the problem-solving process. A well-defined problem serves as the foundation for effective resolution.
D3: Develop Containment Actions
Discipline D3 calls for immediate action to contain the problem and prevent it from escalating further. This step involves implementing short-term measures to mitigate the issue’s impact. Quick containment actions help to stabilize the situation, thus creating a conducive environment for in-depth problem analysis.
D4: Determine and Verify Root Causes
In D4, the team employs various problem-solving tools, such as the 5 Whys or cause-and-effect diagrams, to identify the root causes of the problem. This step is critical in understanding the underlying factors contributing to the issue, enabling the team to address the problem at its source.
D5: Develop Corrective Actions
Once the team identifies the root causes, they use discipline D5, where they are tasked with generating practical solutions comprehensively to address these root causes. The focus is on creating corrective actions that will lead to a sustainable problem resolution.
D6: Implement Corrective Actions
Discipline D6 involves putting the selected corrective actions into action. This step includes developing an action plan, assigning responsibilities, and monitoring the effectiveness of the implemented solutions. Timely execution is crucial in achieving a successful resolution.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
To ensure long-term success, discipline D7 emphasizes implementing preventive measures. These measures are designed to safeguard against the problem’s recurrence in the future. Preventive actions aim to establish a robust system that minimizes the risk of similar issues arising.
D8: Recognize the Team’s Efforts
The final discipline, D8, focuses on acknowledging and celebrating the team’s achievements in successfully resolving the problem. Recognition not only boosts team morale but also reinforces the importance of the problem-solving process within the organization. It catalyzes continuous improvement.
When to use the 8D Approach
- It is best suited for addressing significant issues that demand immediate resolution, especially when traditional methods have failed.
- Typical scenarios where 8D is valuable include product defects, customer complaints, quality control problems, and inefficiencies.
- Instances of safety or regulatory concerns have come to light.
- Warranty concerns have revealed failure rates exceeding expectations.
- Unacceptable internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance, or test failures have been identified.
- The 8D method can be applied reactively, addressing problems that have occurred or proactively preventing potential issues.
Benefits of the 8D Approach
- The 8D approach helps solve problems in a structured way.
- Encourages teamwork and cooperation among people in a company.
- Focuses on finding the real reasons for problems and fixing them for good.
- It uses facts and data to make decisions, not guesses.
- Follow clear steps to remember everything necessary.
- Makes companies better over time by learning from mistakes.
- Leads to better products and happier customers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the benefits of using the 8D approach are numerous. From promoting teamwork and collaboration to enabling data-driven decision-making and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, this problem-solving methodology offers organizations a structured and effective way to address challenges and achieve long-term success.
