Success is not simply a matter of luck or chance. It results from careful analysis, understanding, and implementation of critical elements contributing to achieving desired outcomes. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of successful processes and explore the power of Success and Effect diagram. This powerful tool allows us to identify and analyze the factors contributing to success, enabling us to replicate and optimize those elements in our endeavors. By uncovering the key elements of success and understanding how they interact, we can unlock the secrets to achieving our goals and realizing our full potential. Join us as we explore the intricacies of success and dive deep into the world of the Success and Effect diagram.
Success and Effect Diagram
The success and effect diagram blends fishbone elements, using “five whats” for process analysis instead of the traditional “five whys“. This methodology seeks to uncover the essential elements leading to the success of a process rather than delving into the root causes of problems. This tool holds considerable significance in quality improvement efforts, challenging the common tendency of organizations to prioritize immediate issues at the expense of acknowledging accomplishments.
Using tools and techniques for quality improvement brings a new perspective to continuously enhancing processes by closely examining success. By understanding successful processes, organizations can figure out what works well and use that knowledge to improve other processes. Quality improvement methods help uncover the elements that contribute to success, highlighting the positives rather than just focusing on weaknesses.
Benefits of Success and Effect Diagram
- Identify patterns and best practices for replication in various areas
- Gain insights into effective communication, resource allocation, and strategic decision-making
- Informed decision-making and changes increase the chance of positive results
- A learning mindset helps you stay ahead of the competition and adapt to changes
- Replicate success by understanding underlying principles and strategies
- Transfer knowledge for success in different contexts
2. ATTRIBUTES OF A SUCCESSFUL PROCESS
We asked stakeholders and made a list of things that make processes successful. This list is not everything, but it is an excellent place to begin looking at what makes processes successful.
1. Operational Efficiency: The process generates the required output with minimal resource expenditure, emphasizing “doing the right things right.”
2. Performance Effectiveness: The process fulfills its intended purpose and delivers outputs that align with specified requirements.
3. Cost Management: All costs associated with the process are actively monitored and managed.
4. Consistency: The output demonstrates consistency and reliability.
5. Skilled Workforce with Positive Attitudes: Employee skills align with process requirements and are continuously upgraded with process improvements. Employee attitudes prioritize customer satisfaction and quality.
6. Timeliness: The process consistently produces correct outputs within designated timeframes.
7. Metric Visibility: Performance is measured at various points, and results are visually presented to guide process performers on their operational status.
8. Lean Principles Adherence: Process owners adhere to lean principles, ensuring all process steps contribute value.
9. Optimization of Variables: All variables have been thoroughly studied and statistically optimized.
10. Continuous Enhancement: The process is in a perpetual enhancement state.
11. Innovative Culture Support: The organization fosters an environment that empowers employees to improve continually.
12. Ownership Mentality: Employees exhibit a strong sense of ownership.
13. Application of 5S Principles: There is evidence of applying the 5S principles to the organization and its processes.
14. High-Quality Output Production: The process consistently delivers outputs that meet or surpass customer expectations.
PROCEDURE OF A SUCCESS AND EFFECT DIAGRAM
Following are the best and most commonly used practices for developing cause and effect diagrams:
1. Problem Identification: Identify the problem or process that requires examination.
2. Brainstorming: Engage in a discussion to generate and categorize all possible causes accordingly.
3. Backbone Drawing: Draw a straight horizontal line (the spine or backbone) on the page after identifying the topic. On the right end of this line, draw a rectangle and concisely describe the problem inside it.
4. Adding Causes and Effects: Introduce causes by branching lines off the main backbone at an angle. Write the description of each cause at the end of its respective branch. These causes often correspond to the main categories discussed earlier. Further details related to the cause or effect can be added as sub-categories branching from the main branch. Continue this process until all factors have been documented, resulting in a diagram resembling a fish skeleton.
5. Analysis: Once the diagram is complete, analyze the organized information to derive solutions and formulate action items.
ANALYZING A SUCCESSFUL PROCESS
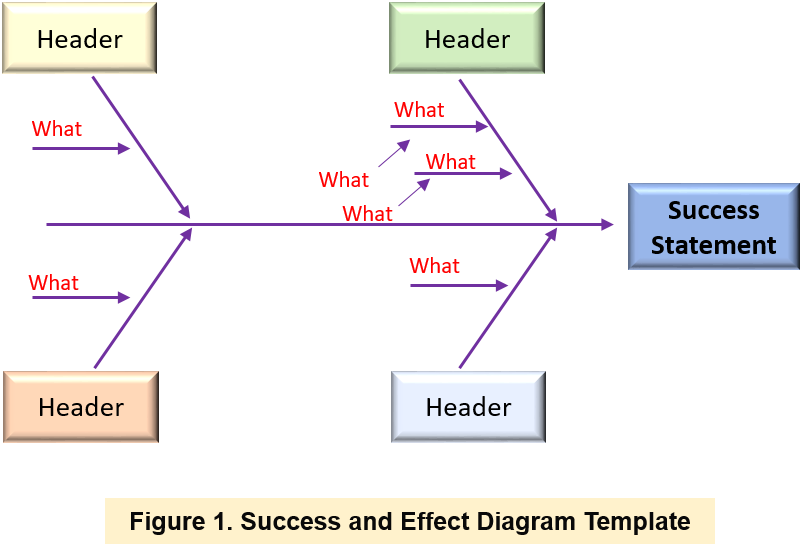
- Illustrate the success as a symptom statement on the right side of the page and enclose it within a box. Connect this success with an arrow to emphasize its role as the focal point for analysis.
- Draw inspiration from the attribute list mentioned earlier to conceptualize the primary successes related to the identified effect. Label these as the main branches in the diagram.
- For each overarching success category, engage in brainstorming sessions to identify potential sub-successes that could impact the issue statement. Apply the five whys technique to explore the underlying causes of each success: What factors led to this achievement?
EXAMPLE
The following figure 2. shows a success and effect diagram crafted to analyze the effective communication process within a top-level organization comprehensively. The team identified four key headers: people, method, material, and machine to delve into what contributed to the success of the process, aiming to pinpoint potential root causes.
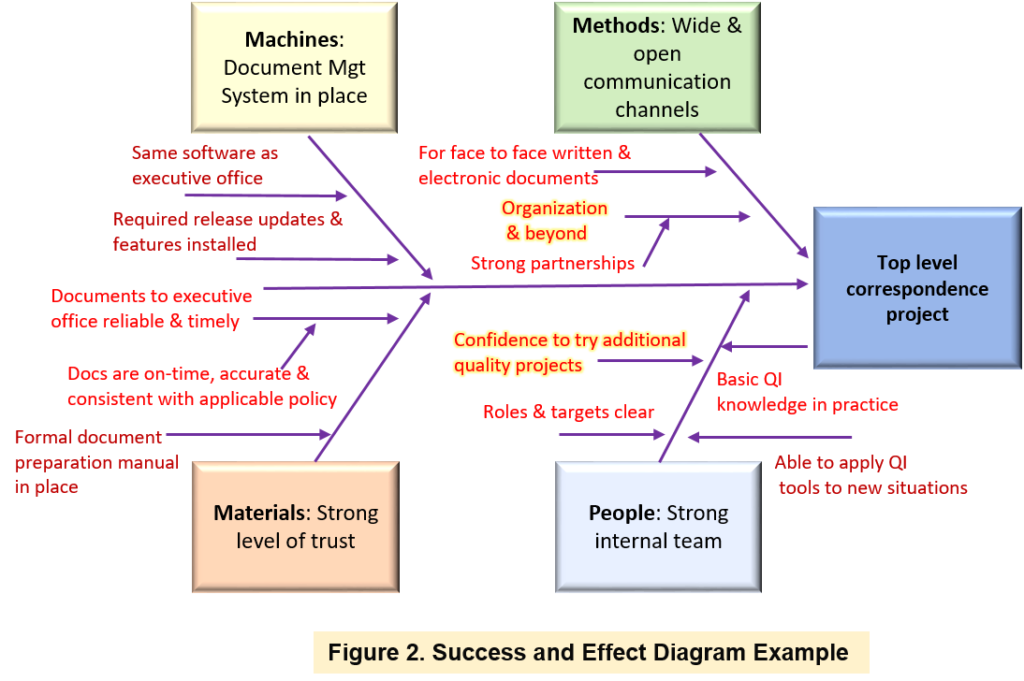
Looking closer at the “materials” header in Figure 2, the team initiated the analysis by identifying an observed success: “Documents are on time, accurate, and consistent with applicable policy.” Subsequently, the team employed a systematic approach to uncover the root success factors, as depicted in Figure 3:
- Observed Success: Documents are timely, accurate, and consistent with applicable policy.
- Visible Success: Meets the customer’s requirements.
- First-level Success: People processing documents are appropriately trained.
- Higher-level Success: Customer needs are comprehended, and service-level targets are established and monitored.
- Highest-level Success: Customer needs are regularly collected and reported to those executing the process.
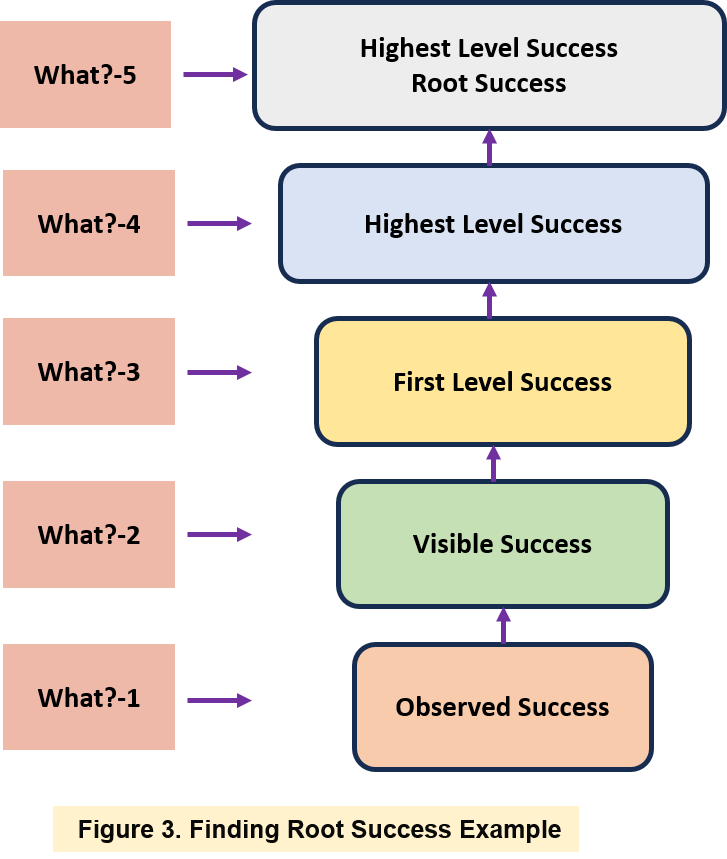
This methodical progression allowed the team to dissect the observed success and identify the underlying factors contributing to the overall effectiveness of the organization’s communication process.
MULTIPLE ROOT SUCCESS
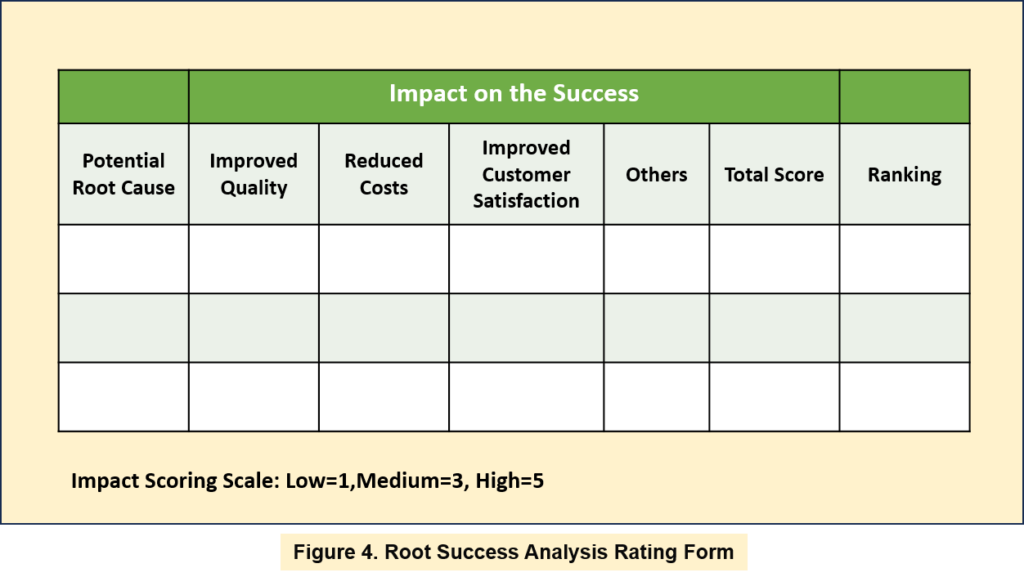
1. Recognize that optimal process performance often hinges on multiple root successes rather than a single factor.
2. Analyze each main category to identify the key elements contributing to its success.
3. Understand that successful processes frequently involve compound successes, where different factors converge to drive overall success.
4. Utilize an interrelationship diagram to explore connections between identified root successes, uncovering potential patterns and interconnections.
5. Consider employing the Root Success Analysis Rating Form (Figure 4) to systematically prioritize and evaluate potential root causes based on various impact dimensions.
6. Evaluate each potential root cause using the rating form, assigning scores to assess their impact.
7. Use the scoring system to rank potential root successes, with the attribute exerting the most significant impact receiving the top rank.
CONCLUSION
The Success and Effect Diagram offers a unique approach to quality improvement by focusing on the elements contributing to the success of a process rather than troubleshooting problems. This methodology brings a fresh perspective, encouraging organizations to recognize and replicate successful patterns. Organizations can optimize processes more effectively by identifying best practices and gaining insights into communication, resource allocation, and decision making. The characteristics of a successful process, ranging from operational efficiency to a culture of continuous improvement, provide a comprehensive guide for organizations striving for excellence. Implementing the procedures of a Success and Effect Diagram enables organizations to unravel the secrets behind success, fostering a positive work environment and continuous enhancement.
