Benchmarking is a valuable tool for businesses to stay competitive in today’s fast-moving market. It involves comparing your company’s performance to top-performing competitors and industry standards. This helps you find areas where you can improve and set achievable goals for success. But remember, there isn’t just one way to do benchmarking. There are different types of benchmarking, each with its purpose. This guide will look at these benchmarking types, their advantages, and how to use them effectively. Whether a small startup or a big company, this guide will teach you how to use benchmarking for ongoing improvement and success.
What is Benchmarking?
Benchmarking is a powerful tool in Lean Six Sigma that allows businesses to measure their performance against competitors or industry standards. It involves identifying the best practices, processes, and performance metrics of top-performing companies and using that information to improve one’s own performance.
Benchmarking can aid organizations in identifying sectors, systems, or operations that need enhancement, potentially leading to either incremental (progressive) improvements or dramatic (business process reengineering) changes.
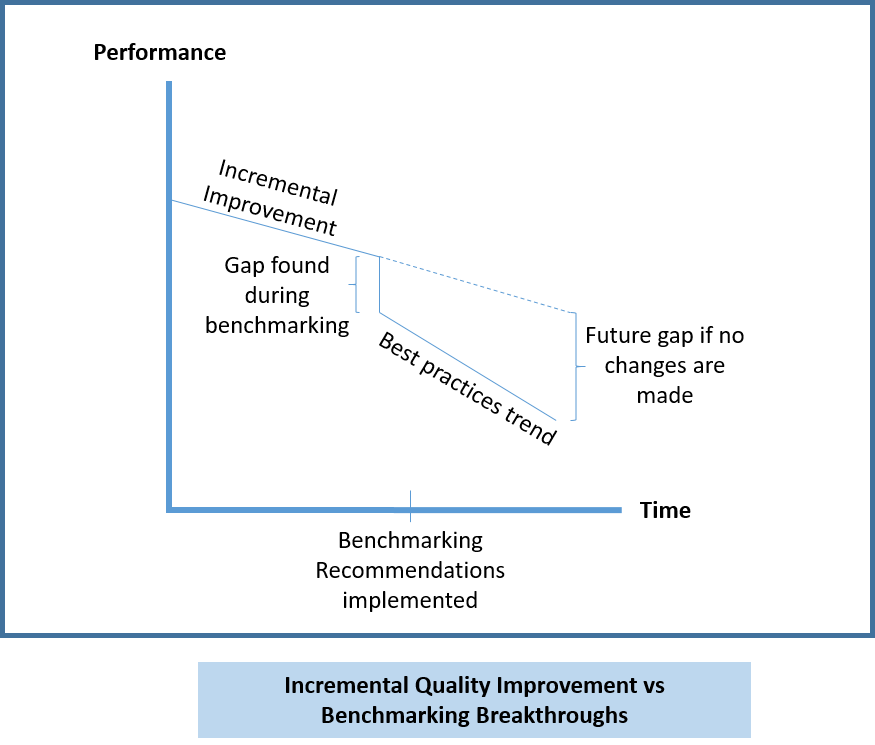
Benchmarking is typically categorized into two types i.e., technical benchmarking and competitive benchmarking. Tools such as the House of Quality matrix and Gantt charts are frequently employed to map out the evaluation of benchmarking activities.
Importance of Benchmarking
- Systematic analysis of business performance against industry benchmarks.
- Identification of areas requiring improvement compared to competitors.
- Establishment of achievable performance targets aligned with industry best practices.
- Maintenance of competitiveness by meeting or exceeding industry standards.
- Acquisition of new ideas and strategies from successful industry peers.
- Promotion of a continuous improvement mindset within the organization.
- Gaining insights into both the company’s and competitor’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Ensuring market relevance by adapting to changing trends and consumer demands.
Types of Benchmarking
Competitive Benchmarking

Businesses compare their performance against direct competitors in this type of benchmarking. By analyzing competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, organizations can gain insights into market trends, customer expectations, and areas where they can earn a competitive advantage.
Technical Benchmarking
Technical benchmarking refers to the process of comparing the technical aspects of a company’s products, services, or processes against those of leading companies, typically within the same industry. The goal of technical benchmarking is to gain insights into how a company can improve its technical capabilities, enhance product quality, increase efficiency in production, and innovate in product development. By examining the technical strengths and weaknesses relative to industry standards or leaders, a company can identify opportunities for technological advancements and process improvements that can lead to a competitive advantage.
Benefits of Benchmarking
Benchmarking is valuable for businesses of all sizes and industries.
- It involves comparing your organization’s performance with industry leaders and competitors.
- This process provides insights for improvement and growth.
- One key benefit is pinpointing areas needing improvement.
- You can compare processes, strategies, and performance metrics.
- This helps set realistic goals and develop targeted improvement plans.
- It tracks changes over time and the effectiveness of efforts.
- Gaining a competitive advantage is another significant benefit.
- You can adopt successful practices from industry leaders.
- It fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
- It encourages exploration of new ideas, and seeking best practices.
Strategies for Effective Implementation
Effective Benchmarking Strategies are:
Clear Goal Definition
- Before you start, make sure to clearly outline your goals and objectives.
- Identify the specific areas or processes you want to improve.
- Goal clarity helps focus efforts and select relevant benchmarks.
Selecting Relevant Competitors
- Choose benchmarks from companies or organizations similar in size, industry, and market position.
- Consider internal (within your organization) and external (industry standards or competitors) benchmarks for a comprehensive perspective.
Establishing a Benchmarking Team
- Create a benchmarking team or task force.
- Include individuals from various departments or areas of expertise for a well-rounded analysis.
- Define the roles and duties of each team member clearly.
- Encourage collaboration and open communication throughout the process.
Data Collection
- Gather data and information from selected benchmarks.
- Utilize methods such as surveys, interviews, or site visits.
- Ensure data accuracy and reliability for meaningful insights and comparisons.
Analysis and Gap Identification
- Analyze collected findings to identify performance gaps or areas for improvement.
- Compare your organization’s performance against benchmarks.
- Find the best methods and practices that can be incorporated into your processes.
Implementation Planning
- Develop an action plan outlining specific strategies to address identified gaps.
- Distribute responsibilities among team members and set a timeline for carrying out the implementation.
- Regularly monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
Track performance
- Continuously review and update your benchmarks.
- Ensure the benchmarking process remains relevant and effective for driving continuous improvement.
Business Benchmarking Example
Consider a restaurant looking to improve its customer service and overall dining experience. After benchmarking, they discovered that a popular fast-food chain consistently serves orders in half the time it takes them. Further research reveals that a renowned fine-dining restaurant manages to turn tables and serve multi-course meals much faster than their establishment. The restaurant adopts several strategies to enhance its efficiency, such as implementing a streamlined kitchen workflow, investing in faster cooking equipment, and retraining its staff to prioritize speed without compromising food quality. This allows them to provide quicker and more enjoyable dining experiences, ultimately becoming more competitive in their market segment.
Conclusion
Benchmarking is a dynamic tool that empowers businesses to stay competitive by comparing their performance to industry leaders and competitors. By pinpointing areas that require enhancement and establishing achievable objectives, and fostering a culture of continuous learning, benchmarking drives growth, enhances performance, and provides a competitive advantage. Understanding the different types of benchmarking and their applications, along with practical strategies for implementation, is critical to harnessing the full potential of benchmarking for ongoing improvement and success in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.


