When developing a successful product or service, meeting customer needs and expectations is paramount. This is where Quality Function Deployment (QFD) comes into play. QFD is a systematic approach that helps businesses translate customer requirements into specific actions and design features. However, understanding the intricacies of QFD can often take time and effort. This comprehensive blog post will demystify QFD by exploring its essential components and methodology in four distinct phases. From understanding customer needs and prioritizing them to developing design parameters and implementing improvements, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to effectively utilize QFD in your business. Get ready to unlock the power of QFD and enhance customer satisfaction through an informed, systematic approach to product development.
Table of Content
- History of QFD
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
- Four Phases of QFD
- Key components of QFD
- When to use QFD
- Advantages of QFD
- Disadvantages of QFD
- Conclusion
History of QFD
Originating in Japan during the 1960s, Quality Function Deployment (QFD) made its way to the United States in the early 1980s, gaining popularity primarily in the automotive sector. American car manufacturers, inspired by the success of companies like Toyota and Mitsubishi, adopted QFD to enhance customer focus in their operations.

Implementing QFD led to notable efficiencies, including significantly shorter design periods and a reduced need for manpower in the design process. This shift from a primary focus on cost to prioritizing customer satisfaction fueled innovation. It boosted the sales of American cars, especially following the rise in popularity of Japanese vehicles in the 1970s.
In contemporary times, QFD and the House of Quality are utilized across various sectors and form an integral part of the Six Sigma methodology.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
In the world of product development and quality management, QFD is a robust methodology that can significantly enhance the success of a project. It is a systematic approach that helps organizations align customer needs and expectations with the design and development process. Doing so ensures that products or services meet customer requirements and exceed their expectations.
QFD is a tool that facilitates effective communication and collaboration among cross-functional teams, including product designers, engineers, marketers, and customer representatives. It provides a structured framework for translating customer needs into specific design requirements, enabling organizations to develop products that truly resonate with their target audience.
Four Phases of QFD
To effectively implement QFD, it is crucial to understand the four phases involved in the process.
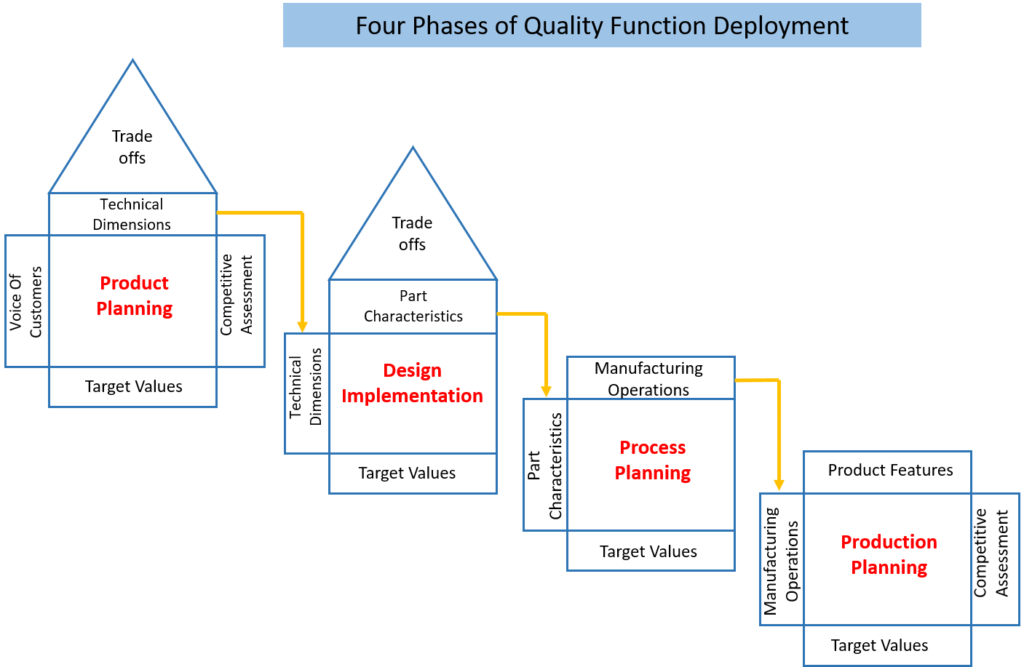
Phase 1 : Planning Phase
The Planning Phase is the cornerstone of the QFD process. It begins with thoroughly gathering customer feedback to develop the Voice of the Customer (VOC), providing deep insights into what customers are looking for in a product. This phase also includes a competitive analysis, where the company assesses its competitor’s strengths and weaknesses. This analysis helps pinpoint areas where the company can excel over its competitors. The primary objectives in this phase are to prioritize customer requirements, define specific product requirements, and create a customer-focused product roadmap, laying the groundwork for the subsequent phases.
Phase 2 : Design Implementation
In this phase, the product’s design is refined by selecting appropriate assemblies, systems, sub-systems, and components.
This phase involves detailed analysis at different levels:
- System Level: This includes examining the product’s technical requirements, prioritizing these specifications, and understanding their effects on specific systems or assemblies.
- Sub-system Level: Complex systems are broken down into sub-systems. This step involves listing, ranking, and analyzing essential components.
- Component Level: Here, the focus is on determining the component’s characteristics to be purchased providing critical information to suppliers.
Phase 3 : Process Planning
This phase is critical to the Quality Function Deployment (QFD) process. It focuses on linking various processes or steps to the technical and functional specifications of the product. This is crucial for identifying the most effective processes for meeting part requirements.
Key activities in this stage include:
- Analyzing important processes
- Determining the flow of these processes
- Assessing the need for production equipment
- Creating a framework for significant processes
Phase 4 : Production Planning
This final phase of QFD involves setting and maintaining quality control throughout the product’s production process. Essentially, this stage sets quality targets for production planning. The activities carried out include:
- Reviewing vital technical and process characteristics;
- Establishing methods for process control;
- Conducting analysis and tests on the process and related parameters.
Key components of QFD
To successfully implement QFD, several key components need to be considered:
Voice of the Customer (VOC)
The initial step in constructing the house of quality, and hence the whole Quality Function Deployment (QFD) process, involves establishing the Voice of the Customer (VOC). This encompasses a comprehensive summary of customer needs, desires, preferences, and expectations of a product or service.
To accurately formulate the VOC, it is essential to prepare a thorough market research report, utilizing a sufficiently large sample size to ensure the reliability of the data.
Several methods can be employed to collect customer feedback for the VOC, such as:
- Conducting surveys
- Performing user interviews
- Organizing focus groups
- Analyzing customer reviews
- Gathering feature requests
- Utilizing sales feedback
- Examining product analytics
Upon identifying specific customer requests, you can ask customers to rate the importance of these items or rank them yourself based on their significance. These factors are then cataloged on the left side of the house of quality matrix, each accompanied by a weighted significance score.
It is important to develop the VOC accurately. Misrepresenting customer feedback can distort your market research outcomes, leading to ineffective implementation of the QFD.
House of Quality (HOQ)
The HOQ is a matrix that serves as the central tool in QFD. It captures the relationship between customer requirements and the technical features or characteristics of the product. The House of Quality typically takes the form of a matrix or diagram and consists of several components, which are represented graphically. It is a powerful tool that helps organizations prioritize customer requirements and align them with technical and competitive benchmarks to deliver superior quality products or services.
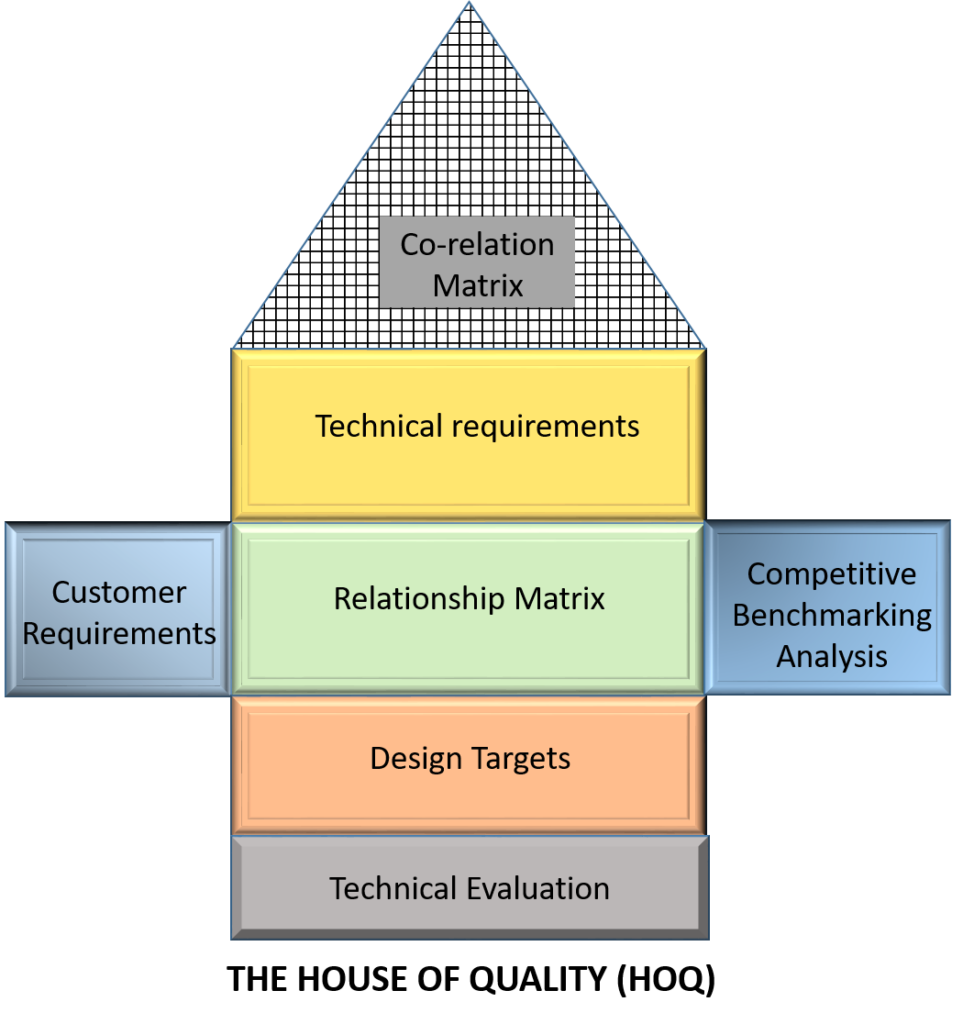
In the house of quality framework, various components are strategically placed to facilitate the Quality Function Deployment (QFD) process:
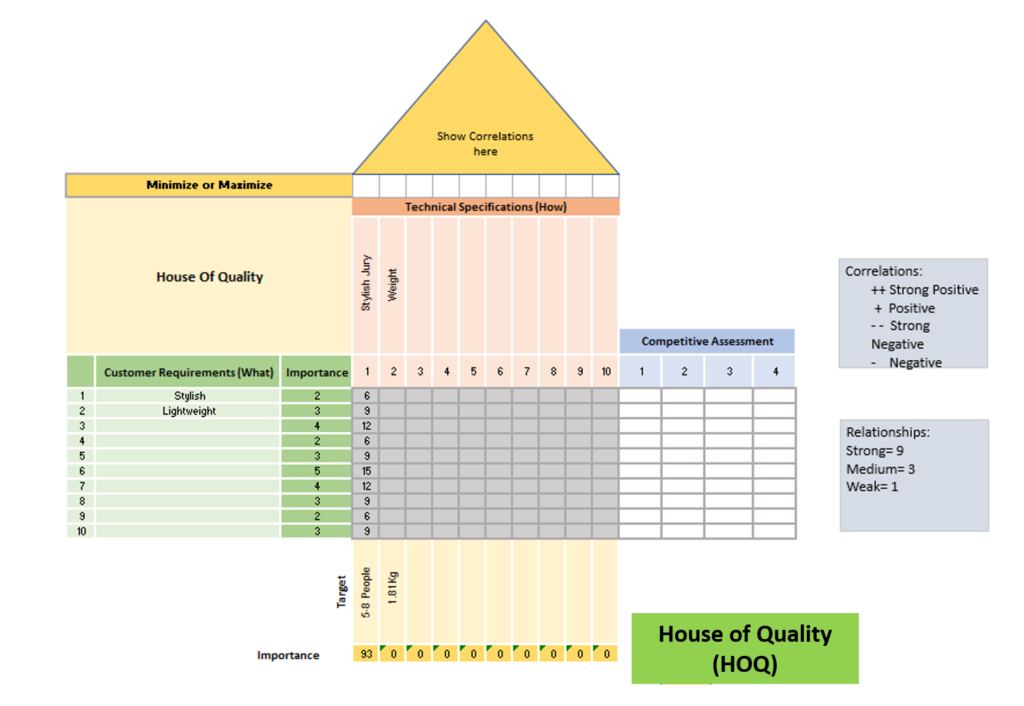
- Left Side: Here, you will find a list of customer-requested features, each assigned a weighted value indicating its importance. This section is commonly referred to as the “Hows.”
- Right Side: This area is dedicated to competitive analysis. It involves assigning weighted values to assess the strengths or weaknesses of the features requested by customers.
- Attic: Known as the “Whats,” this section encompasses control factors such as product design or engineering specifications.
- Main Room: At the core, the relationship matrix evaluates the correlation between customer-requested features (Hows) and control factors (Whats). A high score indicates a strong impact of a control factor in meeting a specific customer request, signifying its significant influence on customer satisfaction.
- Roof: Overseeing the structure, the roof symbolizes the interrelationships between control factors, offering insights into how different aspects of product design or engineering affect each other.
- Foundation: The importance rating at the base is calculated by multiplying scores in the relationship matrix by their weighted importance. A higher number indicates a greater development priority for the feature or factor.
When to use QFD
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is best used in product development once customer needs are clearly defined. It is most effective when applied continuously throughout a product’s lifecycle, consistently focusing on the customer’s perspective. QFD suits iterative innovation well, where customer feedback is abundant. It is more challenging for new product categories with no prior customer reference, but using existing customer insights still adds value.
Advantages of QFD
- Boosts product quality
- Organizes data systematically
- Analyzes competitive quality
- Reduces wastage
- Increases customer satisfaction
- Shortens development cycles
- Encourages unanimous decisions
- Decreases startup costs
- Promotes teamwork
Disadvantages of QFD
- Vague qualitative categories
- Complex matrix structure
- Team opinion conflicts
- Limited applicability
- Labor-intensive process
- Overly comprehensive method
- Time-consuming
- Relies on qualitative data
Conclusion
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a potent methodology aligning customer needs with product development. Its four phases: Planning, Design Implementation, Process Planning, and Production Planning, provide a structured approach. Key components like the Voice of the Customer and the House of Quality prioritize requirements. QFD offers benefits such as improved product quality and customer satisfaction, but it requires careful implementation due to potential complexities and time-consuming aspects. Overall, QFD is a valuable tool for organizations committed to delivering customer-centric products.


