In a world filled with endless choices and decisions, navigating through the complexities of decision-making can be overwhelming. Whether it is choosing between job offers, selecting the perfect vacation destination, or even deciding what to have for dinner, we all face countless decisions every day. That is where the decision matrix comes in. This powerful tool provides a structured approach to decision-making, enabling you to make informed choices based on a set of criteria. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the decision matrix and decode its steps, giving you a comprehensive guide on how and when to use it. Through practical examples and real-life scenarios, you will gain the knowledge and confidence to make sound decisions that match with your objectives and priorities. Prepare yourself to discover hidden insights of effective decision-making with the decision matrix!
What is a Decision Matrix?
When faced with a complex decision that requires careful consideration of multiple factors, a decision matrix can be a handy decision making tool. It visually represents different options and their corresponding criteria, allowing you to assess and compare them objectively and make informed choices by using a structured approach. The decision matrix consists of a grid, with the options listed on one axis and the criteria on the other. Each cell in the matrix is then filled with a rating or score based on how well each option meets each criterion. These ratings are then weighted, reflecting the relative importance of each criterion, and multiplied to calculate a final score for each option. The option with the highest score is considered to be the most favorable choice.
Decision Matrix is also called as:
- Pugh Matrix
- Decision Grid
- Selection Matrix or Grid
- Problem Matrix
- Problem Selection Matrix
- Opportunity Analysis
- Solution Matrix
- Criteria Rating Form
- Criteria-Based Matrix
When to Use a Decision Matrix?
1. It is used to select a single option from a list of choices.
2. It is used when initial list of options has been condensed through prior screening or selection.
3. It is used when you must approach the decision logically rather than relying on intuition.
4. It is used when prioritizing, implementing a solution, or developing a single product.
Steps to Create a Decision Matrix
Step 1: Define the Decision
Identify the decision you need to make. Let us take an example and consider the decision of choosing the best candidate for a job position. List all the candidates who are being considered for the job. These will be the rows in your decision matrix.
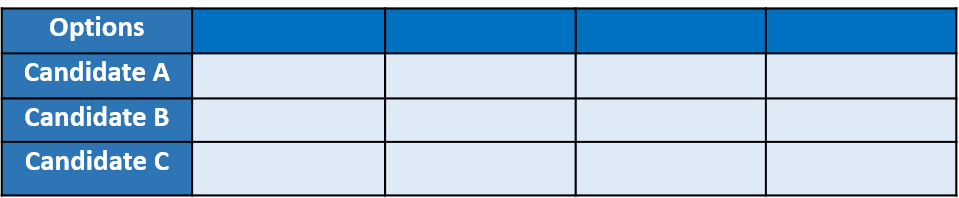
Step 2: Identify Key Criteria
Determine the criteria that will influence your decision. For the job candidate selection, you might consider criteria such as experience, qualifications, skills, and cultural fit.
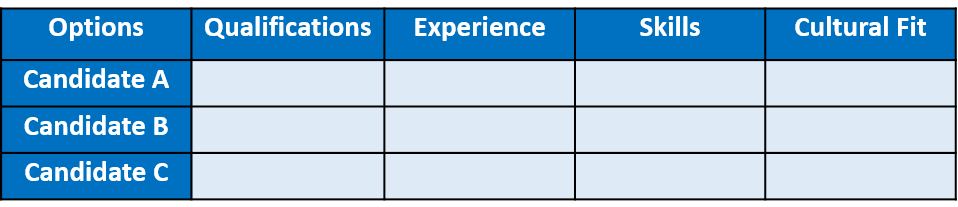
Step 3: Assign Relative Weights
Assign relative weights to each criterion based on their importance. In this case, you might decide the criteria on the scale from 1 to 4 with 4 being the high point and 1 being the low point.
- Qualifications: Weight 4
- Experience: Weight 3
- Skills: Weight 2
- Cultural Fit: Weight 1
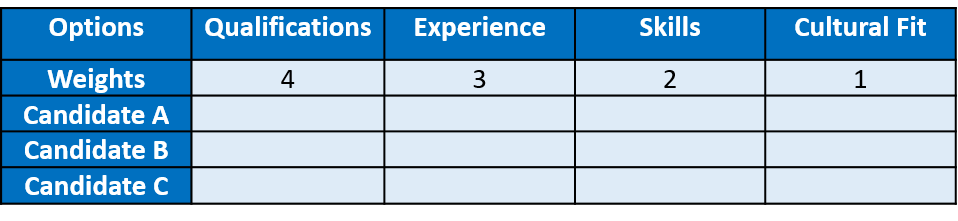
Step 4: Evaluate Alternatives
Assess each candidate against each criterion one by one. Use a rating scale from 1 to 5, with 1 being the lowest and 5 being the highest. For example:
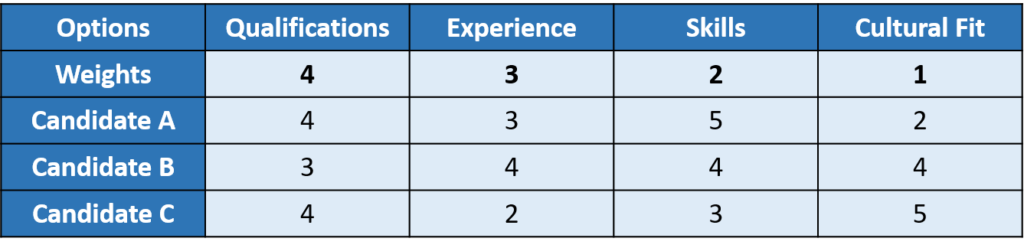
Step 5: Calculate Weighted Scores
Multiply the scores of each candidate by their respective criterion weights. This will give you the weighted scores for each candidate.
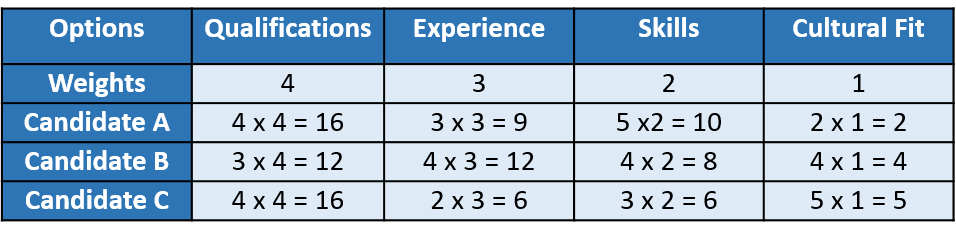
Step 6: Determine the Best Option
Sum up the weighted scores for each candidate to obtain a total score. The candidate with the highest total score is the best choice based on the defined criteria and their weights.

In this example, Candidate A have the highest total score of 37, making him to the top choices based on the defined criteria and weights. Further discussions or assessments may be necessary to make the final decision.
Consistency in your rating scales is crucial. When defining your criteria and rating scales, ensure that the top end of the scale (5 or 3) consistently represents the rating that would most likely lead to the selection of an option. This means that the highest rating should indicate the highest importance, the least difficulty, and the greatest likelihood of success.
Example of Decision Matrix application
Suppose you are a product manager tasked with deciding which features to prioritize in product development. In this scenario, a decision matrix can be a powerful tool for making these crucial decisions. List the potential features under consideration and evaluate them based on market demand, technical feasibility, customer impact, and resource allocation. Assign weights to these criteria to reflect their relative importance in your product development roadmap. Subsequently, rate each feature against these criteria. The decision matrix aids in identifying the features that offer the most value and align with your strategic objectives. It ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that the product meets market demands by providing a structured framework for prioritizing and planning product development efforts.

In this simplified example:
- There are Four potential features (Feature A, Feature B, Feature C, and Feature D)
- There are four criteria’s against each feature i.e. Market Demand, Technical Feasibility, Customer Impact, and Resource Allocation.
- Weights are assigned to each criterion based on their relative importance.
- Scores (1-5)are assigned to each feature based on their performance against each criterion.
- The Total Score column calculates the weighted scores for each feature.
- In this example, Feature C has the highest total score of 39, making it the top priority for product development.
Factors to Consider in a Decision Matrix
When choosing a problem or an area for improvement, consider factors such as:
When selecting a problem or opportunity, consider:
- Team’s control
- Financial potential
- Required resources
- Customer satisfaction impact
- Problem urgency
- Team commitment
- Management support
- Solution complexity
- Resolution time estimate
While choosing a solution, consider factors like:
- Addressing root causes
- The Extent of problem resolution
- Implementation cost and ROI
- Ease of implementation and maintenance
- Team support and control
- Impact on safety, training, and other systems
- Effects on customers and suppliers
- Overall potential challenges
Conclusion
A decision matrix is a powerful tool that helps us make informed choices by systematically evaluating options based on predefined criteria. It is helpful in various situations, from job candidate selection to product feature prioritization. Assigning weights to criteria and comparing alternatives provides a methodical approach to decision-making, guaranteeing that decisions align with our objectives and priorities. Ultimately, the decision matrix aids in making more effective and objective choices in a world filled with countless decisions.