Every organization strives for success and aims to achieve its strategic goals. However, to effectively measure and manage performance, it is essential to have a comprehensive framework in place. This is where the Balanced Scorecard becomes essential. The Balanced Scorecard (BSS) is one of the most popular frameworks for management change, alongside Six Sigma.
BSS is a tool created by Robert Kaplan and David Norton, that provides organizations with a holistic approach to performance measurement by incorporating financial and non-financial metrics. By using this tool, businesses can ensure they are all working towards the same goals, see how they are doing, and make intelligent decisions to succeed. In this blog post, we will look into the intricacies of the Balanced Scorecard and explore how it can unlock organizational success and help to achieve strategic goals.
What is a Balanced Scorecard?

Balanced Scorecard is a comprehensive strategic management framework that enables organizations to reevaluate and refine their strategic objectives and performance measurement methods. It provides a well-rounded approach to measuring organizational success by considering multiple perspectives beyond financial indicators. It supplies input regarding internal operational procedures and external consequences to enhance strategic effectiveness and outcomes consistently.
The history of Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard, initially conceptualized by Dr. Robert Kaplan from Harvard University and Dr. David Norton, emerged as a framework for evaluating organizational performance through a more comprehensive array of performance indicators. Unlike the traditional focus on short-term financial performance as the sole measure of success, the Balanced Scorecard introduced additional non-financial strategic metrics to emphasize long-term achievement. Over time, this system has developed into a fully integrated strategic management approach.
This innovative strategic management method was initially articulated in a series of writings and books by Drs. Kaplan and Norton, building upon the foundational work of Art Schneiderman at Analog Devices. Recognizing the limitations and lack of clarity in previous management approaches, the Balanced Scorecard offers a clear roadmap regarding what aspects companies should assess to achieve a “balance” in their financial perspective.
Kaplan and Norton explain the innovation behind the balanced scorecard in the following way:
“The balanced scorecard retains traditional financial measures. But financial measures tell the story of past events, an adequate story for industrial age companies for which investments in long-term capabilities and customer relationships were not critical for success. These financial measures are inadequate, however, for guiding and evaluating the journey that information age companies must make to create future value through investment in customers, suppliers, employees, processes, technology, and innovation.”
Benefits of implementing a Balanced Scorecard
- It provides a comprehensive framework that goes beyond traditional financial metrics.
- It defines and communicates objectives across departments and levels, thus fostering collaboration.
- Effective performance measurement and evaluation are facilitated through multiple perspectives, enabling data-driven decisions.
- It promotes a culture of accountability and ownership by involving individual employees in goal achievement.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) and corrective actions encourage continuous improvement and learning.
- It empowers organizations to achieve strategic goals and long-term success.
Key components of the Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard model promotes positive conduct within an organization by segmenting it into four distinct areas, often referred to as legs, which are:
- Financial
- Customer
- Internal Business processes
- Learning & growth
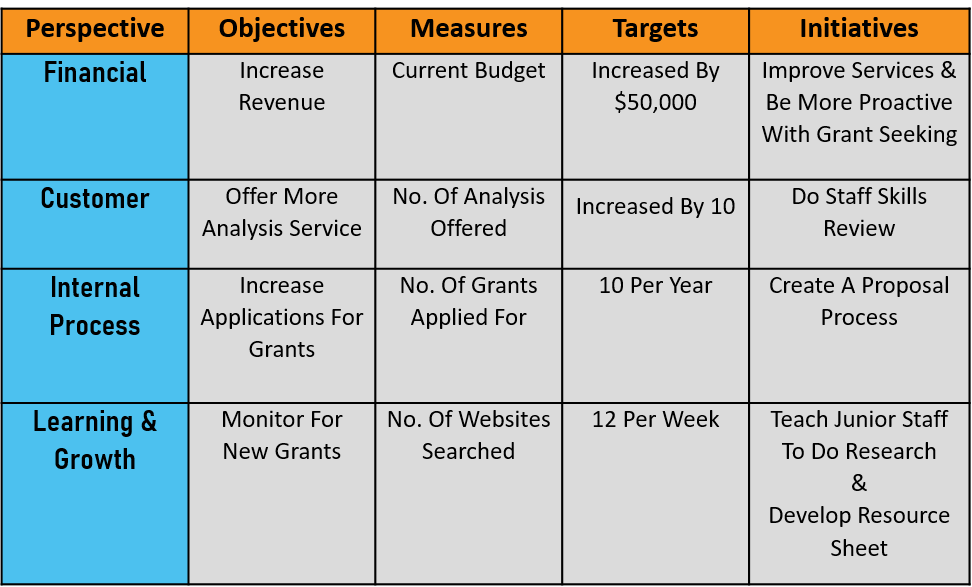
Four critical components of the Balanced Scorecard work together to assess and improve organizational success. Organizations can align their actions and initiatives with their strategic goals, leading to improved performance and overall success.
Financial Perspective:
This component focuses on financial performance indicators such as revenue, profitability, and return on investment. It helps organizations measure their financial health and meet their financial objectives.
Customer Perspective:
This component measures how well an organization meets customer needs and expectations. It includes metrics like customer satisfaction, loyalty, and market share. Organizations can enhance their competitive advantage and improve customer relationships by understanding and addressing customer requirements.
Internal Processes Perspective:
This component examines the internal processes and operations that drive organizational performance. It involves identifying critical functions, measuring their efficiency and effectiveness, and implementing process improvements. By optimizing internal processes, organizations can boost efficiency, cut expenses, and provide superior products or services to clients.
Learning and Growth Perspective:
This component focuses on the organization’s ability to adapt, innovate, and develop human capital. It includes metrics related to employee satisfaction, training and development, and capacity for innovation. By investing in employee skills and nurturing an environment encouraging ongoing learning and advancement, organizations can propel themselves toward enduring prosperity and maintain a competitive advantage.
Implementation of the Balanced Scorecard
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard for Strategic Success of any organization involves the following steps:
1) Introduction
- Using the Balanced Scorecard as an essential tool for strategic management.
- Measuring and monitoring performance across various perspectives.
2) Define Strategic Objectives
- Start by clearly defining organizational strategic objectives.
- Engage stakeholders from different departments and levels.
- Ensure shared understanding of strategy and goals.
3) Translating Objectives into Measures
- Translate strategic objectives into specific performance measures.
- Create targets for each perspective (Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning, and Growth).
4) Communication and Employee Engagement
- Communicate objectives, measures, and targets to all employees.
- Ensure understanding and buy-in through various means (e.g., workshops, regular updates).
- Keep employees aligned and motivated.
5) Establishing a Performance Measurement System
- Select key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with strategic objectives.
- Track progress regularly and collect relevant data.
- Analyze data for meaningful insights to drive decision-making and continuous improvement.
6) Ongoing Process
- Emphasize that the Balanced Scorecard is an ongoing, not a one-time, initiative.
- Conduct regular reviews and updates to keep measures and targets relevant in a changing business environment.
7) Fostering a Culture of Learning and Innovation
- Encourage a culture where employees can suggest improvements and share best practices.
- Drive continuous learning and innovation.
8) Achieving Sustainable Growth
- Effective implementation aligns activities with strategic goals.
- Leads to sustainable growth and organizational success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Balanced Scorecard is a robust framework that empowers organizations to effectively measure, manage, and achieve their strategic goals. By considering financial and non-financial metrics across four critical perspectives – financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth – the Balanced Scorecard offers a holistic approach to performance evaluation. Its benefits include improved alignment, data-driven decision-making, a culture of accountability, and a focus on long-term success. Implementing the Balanced Scorecard requires commitment, collaboration, and ongoing dedication to fostering a culture of learning and innovation. By following its principles, organizations can unlock their potential for sustainable growth and organizational success in today’s dynamic business landscape.


