Tree diagrams are powerful visual tools that help us understand complex concepts and solve problems more efficiently. However, many people need help finding tree diagrams intimidating and confusing. If you have ever felt overwhelmed by tree diagrams or struggled to use them effectively, you are not alone. In this comprehensive guide, we will demystify tree diagrams step by step. We will explain tree diagrams, their helpfulness, and how to create and interpret them. With clear explanations, practical examples, and detailed procedures, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently use tree diagrams in various contexts, from probability and statistics to decision analysis and problem-solving. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply curious about tree diagrams, this guide will give you the clarity and confidence to master this valuable tool.
Tree Diagram
Also called systematic diagram, tree analysis, analytical tree, hierarchy diagram
A tree diagram is a new management planning tool that illustrates how tasks and subtasks are organized to accomplish a specific goal.
Tree diagram is a visual representations of a set of related events or outcomes. They are called tree diagrams because their structure resembles a tree, with a main trunk and branches that branch out further. These branches represent different possibilities or choices that lead to further branches or outcomes.
When to use a Tree Diagram?
- When moving from general understanding to specifics for defined objectives
- In formulating detailed actions, consider steps and dependencies
- When breaking down complex procedures into manageable elements
- When understanding contributing factors through a structured approach
- When evaluating issues for multiple solutions, aiding decision-making.
- While conducting a deep dive into critical issues after affinity diagrams or interrelationship diagram
- In addressing problems or decisions with multiple outcomes
- When systematically breaking down complex problems into manageable parts
- When mapping tasks, dependencies, and milestones for planning in project management
- When enhancing understanding with visual representation
Benefits of Tree Diagram
- Improved Decision Making
Tree diagrams offer a visual structure for decision-making, providing an organized and systematic approach to exploring various options. This facilitates the thorough gathering and analysis of relevant data, aiding in making well-informed decisions for optimal outcomes.
- Effective Troubleshooting
The tree diagram format is a visual guide for problem evaluation and solution exploration. Creating branches for each troubleshooting idea makes the process efficient, increasing the likelihood of identifying and implementing solutions in Comprehensive Analysis. This structured approach ensures that all relevant factors are considered, contributing to a thorough understanding of the issue.
- Visual Representation of Relationships
The visual nature of tree diagrams helps in illustrating relationships between different elements. This clarity aids communication within a team, ensuring everyone understands the connections and dependencies involved in a process or decision
- Efficient Workflow Management
Utilizing tree diagrams simplifies the documentation and replication of workflows. This enables the streamlining of processes, fostering clarity within teams about the most effective methods for handling tasks and projects.
Tree Diagram Procedure
- Clearly state the goal, project, plan, or problem being studied at the top (for a vertical tree) or far left (for a horizontal tree) of your work surface.
- Pose a question guiding you to the next level of detail based on your objective.
- For goals, action plans, or work breakdown structures: “Which tasks are necessary for achievement?” or “How can this be accomplished?“
- For root-cause analysis: “What leads to this?” or “Why does this occur?“
- For a Gozinto chart: “What constitutes the components?” (“Gozinto” originates from “What goes into it?“)
- Generate all possible answers to the question. Use insights from previous diagrams like affinity or interrelationship diagrams, if available. Write each idea below (for a vertical tree) or to the right of (for a horizontal tree) the initial statement.
- Illustrate connections between tiers with arrows, indicating the flow of ideas.
- Verify if all items at this level are necessary for the one above.
- Turn each new idea into a subject statement and ask the question again to uncover the next level of detail. Create additional tiers of statements and show relationships with arrows.
- For each set of items in new tiers, perform a “necessary-and-sufficient” check to ensure logical coherence.
- Keep repeating the process until you reach fundamental elements: specific actions or components that are not divisible or root causes.
- Review the entire diagram and ensure all items are necessary for the objective. All items would be sufficient for the objective if they were present or accomplished.
- Step back and review the complete tree diagram. Make any necessary adjustments or refinements to enhance clarity and coherence.
4. Tree diagram Example
To better understand the tree diagram concept, let us look at a simple and practical example. Imagine planning a weekend trip and considering different modes of transportation to reach your destination.
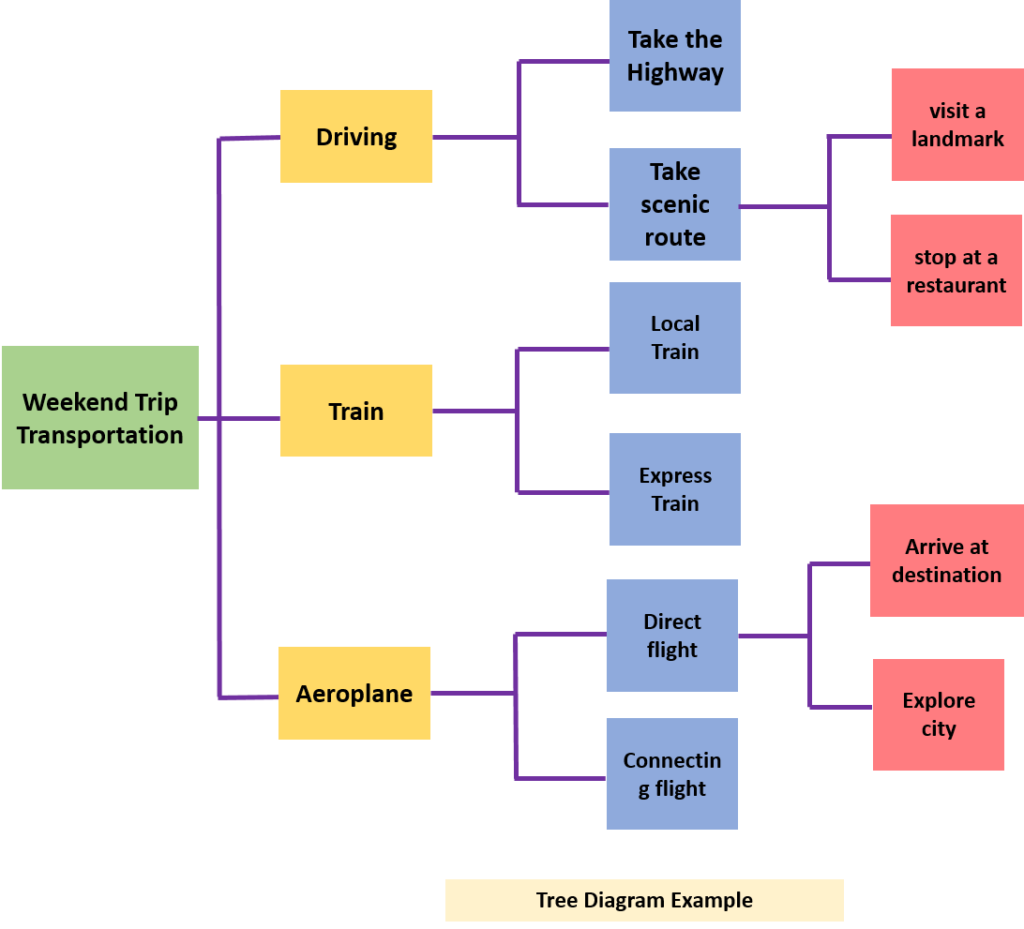
By creating a tree diagram, you can visually map out all the possible paths and outcomes for your weekend trip. It helps you make informed decisions by considering all the available options and their potential consequences.
Conclusion
A tree diagram is a helpful tool for planning and problem-solving, providing a visual breakdown of tasks and subtasks. Its structured approach aids in decision-making, troubleshooting, and comprehensive analysis. The procedure involves defining a central topic, posing questions, brainstorming ideas, and creating tiers of statements with arrows to show relationships. The diagram’s benefits include improved decision-making, efficient troubleshooting, clear representation of relationships, and streamlined workflow management.
