When it comes to making important decisions, having a structured approach is crucial. This is where the Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC) comes in. The PDPC is a powerful tool that helps individuals and teams analyze and visualize the potential risks and challenges associated with a decision or project. In this comprehensive guide, we will demystify the PDPC and provide a step-by-step breakdown of how to utilize it effectively. From understanding the essential components of a PDPC to knowing when and how to apply it in different scenarios, this article will equip you with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions and mitigate potential risks. Whether you are a project manager, business owner, or someone looking to enhance your decision making abilities, this guide will be your go to resource for mastering the PDPC.
What is a Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC)?
The Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC) is a recently introduced management planning tool designed to systematically pinpoint potential issues that could arise during the development of a plan.
The PDPC consists of a series of interconnected branches that represent different decision points and their corresponding actions. It helps identify potential problems or risks while implementing a plan or project. By outlining these potential challenges, the PDPC enables proactive problem solving and contingency planning.
The chart typically starts with the primary goal or objective at the top, with subsequent branches representing different options or courses of action to achieve that goal. Each branch further identifies potential problems or risks associated with that particular action.
By utilizing a PDPC, individuals and organizations can make more informed decisions, considering both their choice’s positive and negative aspects. It aids in minimizing risks, maximizing opportunities, and ultimately improving the overall success rate of any project or plan.
WHEN TO USE PDPC
- Before executing a large and intricate plan
- When the timely completion of the plan is crucial
- In situations where the consequences of failure are significant
- When introducing a new process
- While managing a substantial and detailed project
- When the risks associated with process failure are substantial
BENEFITS OF PDPC
- PDPC visualizes outcomes and critical paths in complex projects
- It assesses and mitigates risks by mapping potential issues and solutions
- Aids in evaluating design and process options in new product development
- Helps to improve existing processes by identifying potential hurdles
- Versatile for various decision-making scenarios, enhancing efficiency and risk management
PDPC PROCEDURE
- Define Main Objective:
Clearly outline the primary goal or problem to be addressed.
- Develop High-Level Tree Diagram:
Create a high-level tree diagram that shows the main objective, second level of main activities, and a third level of broadly defined tasks to accomplish these activities.
- Assess Possible Outcomes for Each Task:
For each task on the third level of your diagram, brainstorm potential issues that could arise.
- Review Potential Problems:
Examine all identified problems, eliminating those that are improbable or have insignificant consequences. Add these problems as a fourth level in your diagram, linked to their respective tasks.
- Brainstorm Countermeasures
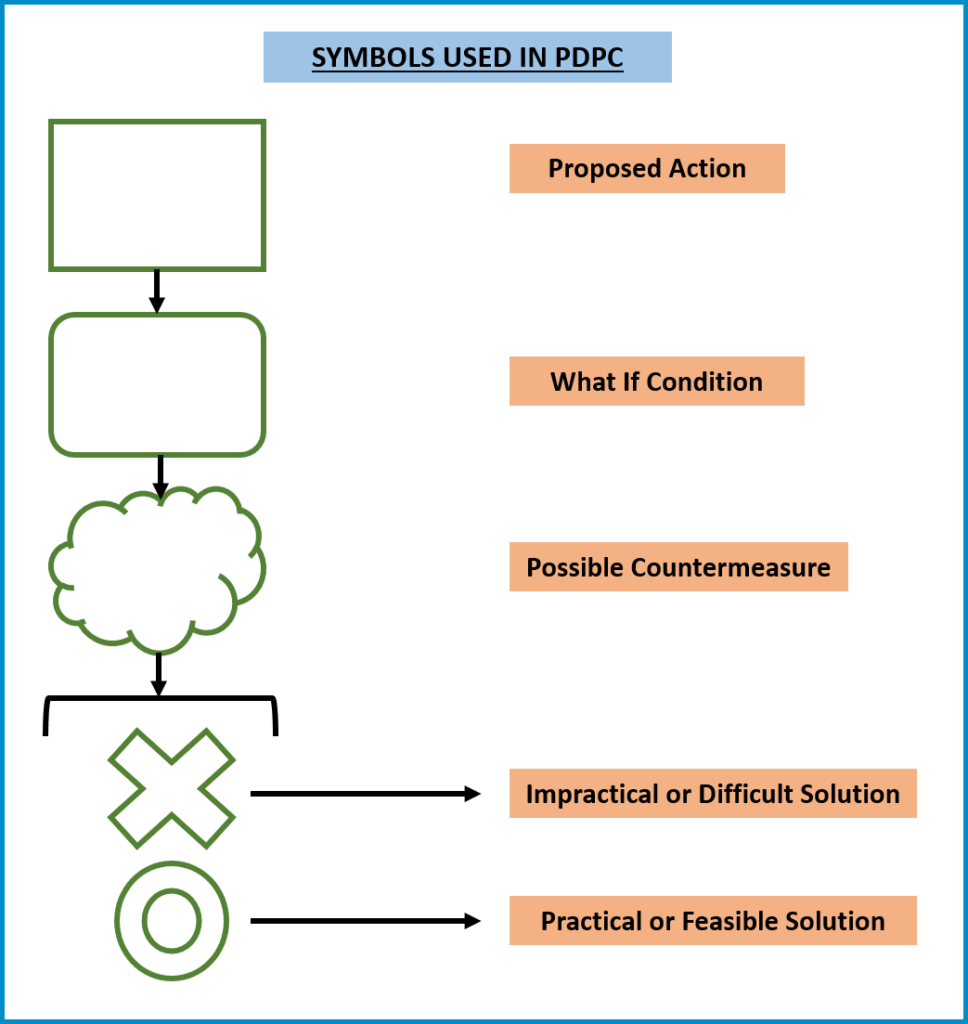
For each identified problem, brainstorm possible preventive or remedial actions. Represent these countermeasures on a fifth level in your diagram, using clouds or jagged lines for visualization.
- Evaluate the Practicality of Countermeasures:
Assess the feasibility of each countermeasure based on cost, time, ease of implementation, and effectiveness. Mark impractical countermeasures with an X and practical ones with an O.
- Create PDPC Chart:
Using the information from your tree diagram, create a detailed PDPC chart. Ensure it visually represents the main objective, tasks, outcomes, risks, and countermeasures in an organized flow.
- Review and Refine:
Critically assess and improve the chart. Seek feedback to ensure all aspects are thoroughly analyzed and represented. By integrating these additional steps, you will have a comprehensive PDPC guide that helps make informed decisions and effectively mitigate risks in complex scenarios.
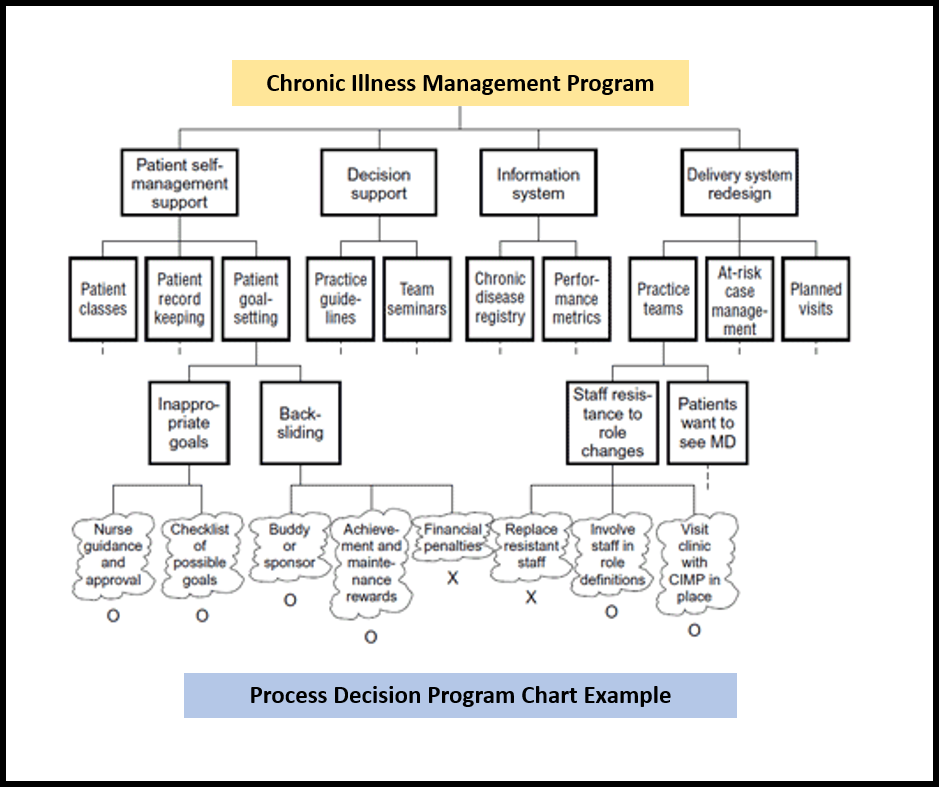
PDPC EXAMPLE
A medical group aims to enhance care for patients with chronic illnesses through a new Chronic Illness Management Program (CIMP). The program comprises four key elements, each with defined components outlined in the Process Decision Program Chart. Some identified issues, like backsliding in goal-setting, led the team to incorporate a buddy system for patients. The chart facilitated strategic planning, including staff visits to clinics with established CIMP programs and proactive training for nurses on counseling patients with inappropriate goals.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC) is a powerful tool for structured decision-making and risk management in both business and individual contexts. By visualizing the decision-making process and potential outcomes, the PDPC aids in proactive problem solving, contingency planning, and overall project success. Its benefits include assessing and mitigating risks, evaluating design and process options, and improving existing processes. The outlined procedure for creating a PDPC provides a systematic approach, guiding users through defining objectives, assessing outcomes, visualizing countermeasures, and ultimately creating a detailed chart for informed decision-making.
